Top 10 Questions About Sinusitis Answered by Experts
Sinusitis is one of those conditions that nearly everyone deals with at some point, yet most people have a lot of unanswered questions about it. Is it the same as a cold? Do you always need antibiotics? Can it become dangerous?
Here are the 10 most common questions about sinusitis — answered clearly and backed by current medical understanding.
1. What Exactly Is Sinusitis?
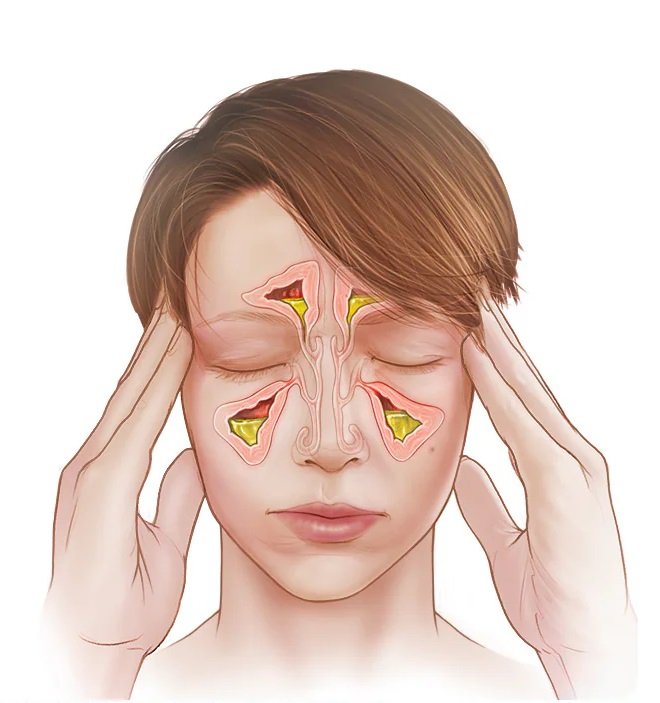
Sinusitis (also called rhinosinusitis) is inflammation and swelling of the tissue lining your sinuses — the air-filled spaces behind your forehead, cheeks, nose, and eyes.
When healthy, your sinuses produce a thin layer of mucus that drains through small channels into your nose. But when the lining gets inflamed (from a cold, allergies, or infection), it swells and blocks those channels. Mucus gets trapped, pressure builds, and bacteria can start to grow in that stagnant fluid.
The result: facial pain, pressure, congestion, and that general feeling of your head being stuffed full of concrete.
2. What’s the Difference Between Acute and Chronic Sinusitis?
The main difference is how long it lasts:
- Acute sinusitis — lasts less than 4 weeks. Usually caused by a viral infection (common cold). This is what most people experience.
- Subacute sinusitis — lasts 4 to 12 weeks. A gray area between acute and chronic.
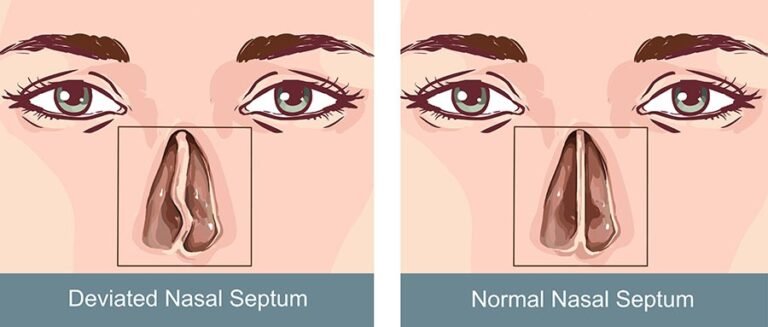
- Chronic sinusitis — lasts 12 weeks or longer, even with treatment. Often involves persistent inflammation rather than active infection. May be linked to nasal polyps, a deviated septum, or immune issues.
- Recurrent sinusitis — 4 or more acute episodes per year, with symptom-free periods in between.
Acute sinusitis usually resolves with home care. Chronic sinusitis often requires a more aggressive approach, including prescription medications or sometimes surgery.
3. How Do I Know If It’s Sinusitis or Just a Cold?
This is one of the most common questions, and the answer comes down to timing and specific symptoms:
It’s probably a cold if:
- Symptoms peaked around day 3–4 and are gradually improving
- Nasal discharge is clear or slightly white
- You feel better within 7–10 days
It’s likely sinusitis if:
- Symptoms last beyond 10 days without improvement
- You have thick yellow or green nasal discharge
- You feel significant facial pain and pressure (not just a stuffy nose)
- Symptoms improved and then suddenly got worse — this “double worsening” pattern strongly suggests a bacterial sinus infection
- You have a high fever (above 102°F) with nasal symptoms
4. What Causes Sinus Infections?
The most common path to a sinus infection looks like this:
- A cold virus inflames your nasal and sinus tissue
- Swelling blocks your sinus drainage pathways
- Mucus gets trapped in your sinuses
- Bacteria multiply in the trapped, warm mucus
- You develop a secondary bacterial sinus infection
Other causes include:
- Allergies — trigger chronic inflammation that blocks sinus drainage
- Nasal polyps — growths that physically obstruct sinus passages
- Deviated septum — restricts airflow and drainage on one side
- Environmental irritants — smoke, pollution, and chemical fumes
- Fungal infections — less common, but can cause chronic sinusitis in some people
5. Do I Need Antibiotics for Sinusitis?
This is probably the most important question on this list, because the answer surprises most people: usually no.
About 70% of acute sinus infections are viral. Antibiotics don’t work against viruses. Current medical guidelines (from the American Academy of Otolaryngology) recommend:
- Watchful waiting for at least 7–10 days with home care (saline rinses, steam, OTC pain relievers)
- Antibiotics only if symptoms last beyond 10 days without improvement, or in cases of severe symptoms (high fever above 102°F with facial pain for 3+ days)
- Antibiotics if symptoms improve then suddenly worsen (“double worsening”)
Overprescribing antibiotics contributes to antibiotic resistance, so it’s actually better for you AND for public health to try home remedies first.
6. What Home Treatments Actually Work for Sinusitis?
These are the treatments with the most evidence behind them:
- Saline nasal irrigation — the gold standard. A neti pot or squeeze bottle physically flushes out mucus, allergens, and bacteria. Use distilled or boiled water only. Need a neti pot? See our review of the top 5 brands.
- Steam inhalation — warm, moist air thins mucus and reduces inflammation. Add eucalyptus oil for extra decongestant effect.
- Warm compresses — placed over the face to relieve sinus pressure and promote drainage
- Staying hydrated — fluids keep mucus thin. Hot herbal teas are especially helpful.
- Rest and head elevation — supports immune function and uses gravity to help sinuses drain
- OTC pain relievers — ibuprofen is preferred because it reduces both pain AND inflammation
For a deeper dive into natural approaches, check out our guide to herbal remedies for nasal congestion.
7. Can Sinusitis Lead to Serious Complications?
In the vast majority of cases, sinusitis resolves without complications. However, in rare situations, untreated sinusitis can lead to:
- Orbital cellulitis — infection spreading to the tissue around the eyes. Signs include eye swelling, redness, and vision changes. This is a medical emergency.
- Meningitis — extremely rare, but infection can spread to the brain’s protective membranes
- Brain abscess — an exceedingly rare but serious complication of frontal sinusitis
- Chronic sinusitis — repeated acute infections can lead to persistent inflammation
- Nasal polyps — chronic inflammation can trigger polyp growth, worsening the problem
Warning signs that need immediate medical attention: swelling or redness around the eyes, severe headache, stiff neck, high persistent fever, or vision changes.
8. How Is Sinusitis Diagnosed?
Most acute sinusitis is diagnosed based on your symptoms and a physical exam — no special tests needed. Your doctor will check for tenderness around your sinuses and look inside your nose.
For persistent or recurring cases, additional tests may include:
- Nasal endoscopy — a thin camera scope inserted into your nose to visualize the sinus openings directly
- CT scan — detailed images that reveal blockages, polyps, or structural abnormalities
- Allergy testing — if allergies are suspected as the underlying cause
- Mucus culture — rarely needed, but can identify specific bacteria in chronic cases that don’t respond to treatment
9. When Does Sinusitis Require Surgery?
Surgery is generally a last resort, reserved for chronic sinusitis that hasn’t responded to several months of medical treatment. It may also be considered for:
- Nasal polyps that are blocking sinus drainage
- A deviated septum that’s contributing to recurring infections
- Fungal sinusitis that requires physical removal of fungal material
The most common procedure is Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS), which uses a tiny camera and instruments to remove blockages and widen drainage pathways. Balloon sinuplasty is a less invasive alternative that uses a small balloon to open up blocked sinus passages.
Success rates for sinus surgery are generally high, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in symptoms.
10. How Can I Prevent Sinusitis?
You can’t prevent every sinus infection, but these habits significantly reduce your risk:
- Wash your hands frequently — the single most effective way to prevent the colds that lead to sinusitis
- Use daily saline irrigation — clears allergens, irritants, and pathogens before they cause inflammation
- Manage allergies — treat them proactively, not reactively
- Keep indoor air moist — use a humidifier to maintain 30–50% humidity
- Avoid cigarette smoke — damages the cilia that move mucus through your sinuses
- Stay hydrated daily — thin, flowing mucus is less likely to get trapped
- Eat immune-supporting foods — vitamin C, zinc, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins
- Don’t overuse decongestant sprays — 3 days maximum to prevent rebound congestion
- Get a flu shot annually — preventing influenza prevents a common sinusitis trigger
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sinusitis contagious?
Sinusitis itself isn’t contagious, but the viruses that cause it are. If your sinus infection was triggered by a cold, you can pass that cold virus to others through sneezing, coughing, or contaminated surfaces. Once the virus causes sinusitis in you, the secondary bacterial infection isn’t transmitted to others.
Can sinusitis cause tooth pain?
Yes, and this catches many people off guard. Your upper teeth roots sit very close to the floor of your maxillary sinuses (the ones behind your cheeks). When those sinuses are inflamed and swollen, the pressure can cause significant aching in your upper teeth. If dental X-rays look normal and the pain coincides with sinus symptoms, sinusitis is the likely culprit.
How long should I wait before seeing a doctor?
Try home remedies for 7–10 days first. See a doctor if symptoms haven’t improved at all after 10 days, if you develop a fever over 101°F, if symptoms get worse after initially improving, or if you experience swelling around your eyes or severe headache. These could indicate a complication requiring prompt medical treatment.
Can stress cause sinusitis?
Stress doesn’t directly cause sinus infections, but chronic stress weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to the colds and infections that trigger sinusitis. Managing stress through adequate sleep, exercise, and relaxation practices supports your body’s ability to fight off sinus-related illnesses.
Is it safe to fly with sinusitis?
Flying with active sinusitis can be very painful. Changes in cabin pressure during takeoff and landing put extra stress on already-inflamed sinuses, potentially causing severe pain, nosebleeds, or even eardrum damage. If you must fly with sinusitis, use a decongestant nasal spray 30 minutes before takeoff and landing, and stay well-hydrated throughout the flight.