Understanding The Role Of Mucus In Nasal Health
The significance of mucus in nasal health often prompts curiosity. Mucus is more than a mere nuisance associated with colds or allergies; it serves a vital purpose in safeguarding the nasal passages against infection and irritation.
This article examines mucus’s composition and role, emphasizes its relevance in maintaining nasal health, addresses potential factors contributing to excessive mucus production, and offers guidance on mitigating and controlling mucus accumulation.
Readers are encouraged to continue reading to acquire insights into preventing mucus accumulation and discerning the appropriate timing for seeking medical intervention in case of persistent symptoms.
What is Mucus?
Mucus is a viscous, gel-like substance secreted by the mucous membranes lining the respiratory system and various other bodily structures. It is vital in maintaining the moisture, protection, and proper functioning of the nasal passages and airways.
Composition and Function
The mucus primarily comprises water, mucin proteins, enzymes, and various cells. These work synergistically to trap and neutralize bacteria and viruses. Concurrently, cilia assist in expelling mucus from the respiratory system.
Mucin proteins are the principal component responsible for mucus’s gel-like texture. They facilitate the entrapment and immobilization of pathogens. Enzymes embedded within mucus perform a crucial function in decomposing these captured microorganisms.
Specialized cells within the mucus layer, such as goblet cells, continuously produce and secrete mucus to uphold the protective barrier. Cilia, microscopic hair-like structures along the respiratory tract, exhibit coordinated beating motions to propel mucus-containing pathogens upward and out of the airways. This process deters infections and upholds the respiratory system’s overall health.
The Importance of Mucus in Nasal Health
Mucus is paramount in nasal health. It is a vital barrier shielding the respiratory system’s mucous membranes from detrimental particles, pollutants, and pathogens, promoting comprehensive respiratory well-being.
Protecting Against Infection and Irritation
Mucus plays a crucial role in safeguarding against infection and irritation by initiating an immune response and reducing inflammation when irritants and pathogens enter the nasal passages.
The mucus’s protective barrier function within the nasal passages is an essential defense mechanism. Upon irritants or pathogens infiltrating the nasal lining, mucus traps and sequesters these harmful entities, impeding their progression into deeper regions of the respiratory system. This entrapment impedes their mobility and facilitates the recruitment of immune cells. Immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages are mobilized to the mucus layer to counteract and eliminate these threats, thereby aiding in preventing infections.
Causes of Excessive Mucus
Overproduction of mucus can be attributed to various factors, such as allergies, sinusitis, infections, and exposure to irritants, all of which may result in discomfort and respiratory complications.
Allergies and Sinus Infections
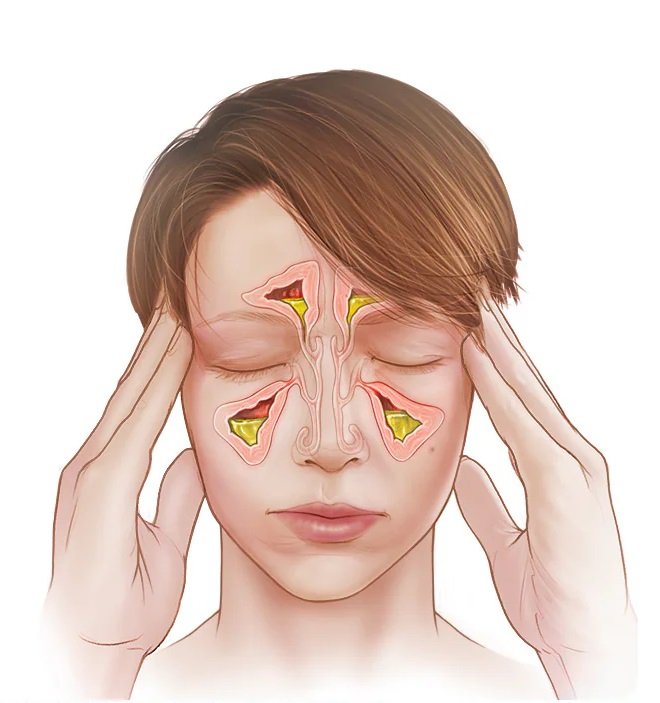
Allergies and sinus infections are significant factors contributing to heightened mucus secretion, which results in nasal congestion and sinus pressure as the body initiates processes to expel allergens and combat infections. This surplus mucus production manifests in symptoms like a runny or congested nose, postnasal drip, and persistent throat clearing. Sinus infections can induce inflammation within the sinus cavities, prompting facial discomfort or sensitivity, headaches, and occasionally fever.
Upon detection of allergens or pathogens, the body prompts the immune system to discharge histamines, provoking the dilation and leakage of blood vessels, thereby intensifying mucus generation. While these reactions serve as the body’s protective mechanisms against potential threats, they frequently lead to discomfort and disruption in daily functioning.
Managing and Reducing Mucus Production
Managing and reducing mucus production entails employing various strategies, such as nasal irrigation, nasal sprays, decongestants, and appropriate humidification. These measures are implemented to uphold optimal mucus flow and respiratory health.
Treatment Options and Home Remedies
Treatment options and home remedies for excessive mucus include saline nasal sprays, humidifiers, and natural remedies like steam inhalation and proper hydration to relieve sinus symptoms. Warm beverages like herbal teas for congestion can also help thin mucus and provide soothing relief.
Saline nasal sprays effectively loosen mucus and ease congestion, reducing sinus pressure. Humidifiers also introduce moisture into the air, which can help thin out mucus. Steam inhalation, such as steam from a warm shower or a bowl of hot water, can also aid in clearing nasal passages.
Adequate hydration is crucial as it prevents mucus from thickening and becoming challenging to expel. Additionally, ensuring good indoor air quality by maintaining cleanliness and eliminating irritants from living spaces can contribute to managing mucus production and supporting sinus health.
When to See a Doctor
While intermittent mucus accumulation is considered within normal bodily functions, persistent or severe symptoms could signify underlying medical conditions such as a sinus infection or chronic sinusitis. In such cases, seeking professional medical evaluation and treatment from a qualified healthcare provider is imperative.
Signs of a More Serious Condition
Persistent nasal congestion, thick or discolored nasal discharge, facial pain, and sinus inflammation are indications of a more severe condition, all of which could suggest an underlying infection or other medical concerns.
Additionally, warning signs to be vigilant about include fever, breathing difficulties, headaches, and a diminished sense of taste or smell. In cases where these symptoms persist or aggravate, seeking a medical assessment is imperative to ascertain the underlying cause. Common underlying factors, such as sinusitis or respiratory viruses, may necessitate medical intervention. Neglecting inflammation in the nasal passages can potentially lead to more severe complications, underscoring the critical importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Mucus Buildup
Preventing the accumulation of mucus entails the adoption of healthy habits and practices, which include:
- maintaining proper nasal healthcare
- ensuring optimal air quality
- supporting ciliary function to maintain a balanced mucus composition and adequate mucus flow
Healthy Habits and Practices
Establishing and maintaining healthy habits and practices to prevent mucus buildup is crucial. These practices include regular nasal cleansing, ensuring adequate hydration to maintain moist airways, and observing good hygiene habits to facilitate airway clearance and promote overall nasal health.
Regular nasal cleansing, which can involve using a saline solution or a neti pot, significantly eliminates excess mucus and allergens from the nasal passages. This process helps alleviate congestion and enhances respiratory ease.
Proper hydration is fundamental in preserving mucus’s thin consistency, preventing it from thickening and becoming adhesive. Additionally, good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and refraining from touching the face, can mitigate the chances of introducing irritants into the nasal passages, thus decreasing the likelihood of heightened mucus production and congestion.