Recognising And Managing Deviated Septum Symptoms
Experiencing difficulty breathing through the nose, frequent nosebleeds, or recurrent sinus infections may indicate the presence of a deviated septum, a prevalent condition characterized by the displacement of the thin wall separating the nostrils.
This article examines the symptoms, diagnostic procedures, available treatment options, and preventive measures associated with a deviated septum. This resource offers comprehensive coverage, whether seeking a comprehensive understanding of the condition or exploring strategies to alleviate its symptoms.
Understanding Deviated Septum
Comprehending a deviated septum is crucial for identifying and addressing the diverse symptoms linked to this prevalent condition characterized by the displacement of the nasal septum. Such deviation can result in complications, including nasal congestion, respiratory challenges, and persistent facial discomfort.
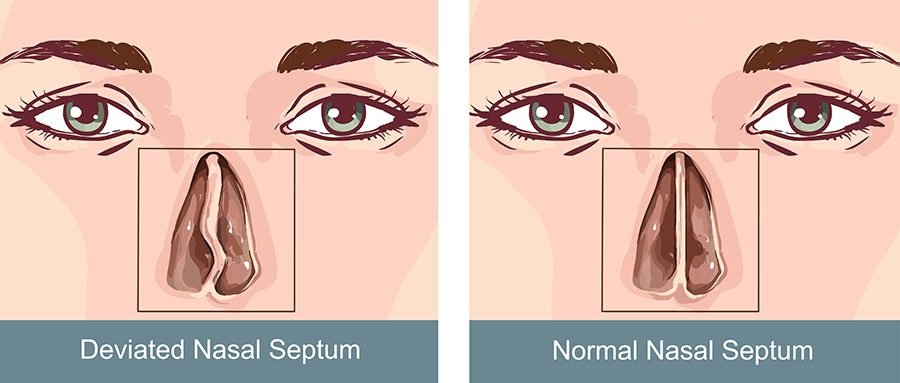
What is a Deviated Septum?
A deviated septum is characterized by the displacement of the nasal septum, comprised of cartilage and bone and divides the nasal cavity into two separate nostrils. This structural component is vital for maintaining proper airflow and providing necessary structural support to the nasal passageways.
Deviations in the septum can arise from various factors, including trauma, where an impact on the nose causes misalignment of the septum or congenital defects present from birth. Additionally, deviations may manifest due to developmental anomalies during childhood or adolescence.
A deviated septum can disrupt nasal airflow, resulting in symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, recurrent sinus infections, and potentially snoring or obstructive sleep apnea.
Signs and Symptoms of a Deviated Septum
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a deviated septum is essential for prompt diagnosis and management. This condition may present various issues, including nasal congestion, breathing difficulties, and recurrent nosebleeds.
Common Indicators
Common signs of a deviated septum include:
- Persistent nasal congestion
- Frequent difficulty breathing through one or both nostrils
- Recurring nosebleeds
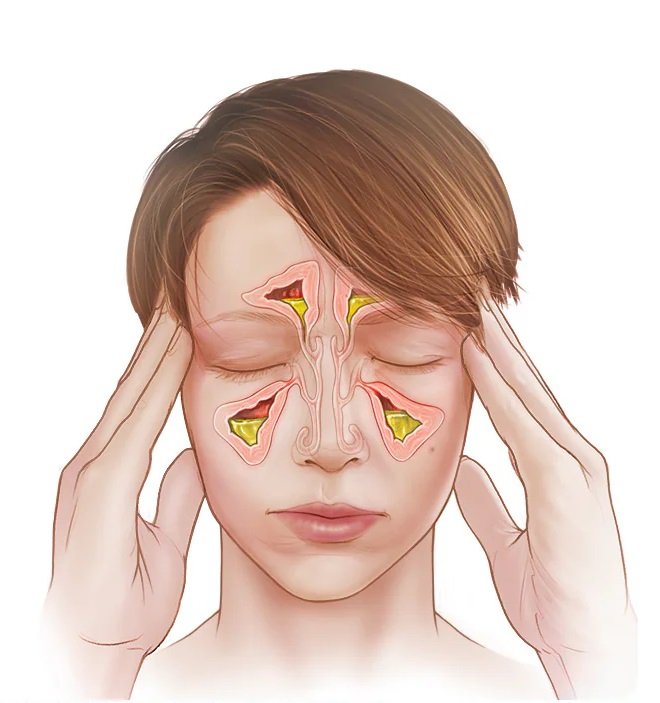
Individuals affected by a deviated septum may also report experiencing facial pain or pressure, notably around the forehead, eyes, or cheeks. This discomfort is often attributed to the compromised airflow and inadequate drainage associated with the condition, which can lead to headaches and sinus infections.
Another prevalent symptom is loud snoring, a consequence of airway obstruction during sleep. Individuals with a deviated septum may also notice a decrease in their sense of smell, which can significantly impact their overall quality of life. It is important to note that these symptoms may vary in severity and frequency and occasionally be misinterpreted as manifestations of allergies or chronic sinusitis.
Diagnosing a Deviated Septum
Diagnosing a deviated septum typically entails a thorough medical assessment performed by an Otolaryngologist (Ear, Nose, and Throat specialist). This professional will assess symptoms and conduct a physical examination, frequently complemented by imaging studies.
Physical Examination and Imaging Tests
A diagnostic assessment of a deviated septum typically involves an examination by an Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist utilizing a nasal speculum or an endoscope to inspect the nasal passages. During this examination, the specialist meticulously evaluates the nasal cavity to identify any structural anomalies or obstructions that may be associated with the deviated septum.
Along with the visual inspection, the ENT specialist may prescribe imaging procedures such as CT scans to obtain a more precise view of the nasal septum’s structure. These imaging studies yield crucial information for determining the degree of deviation and formulating an appropriate treatment strategy. By integrating the findings from the physical examination with the results from the imaging studies, the ENT specialist can devise a comprehensive and individualized plan to manage the deviated septum.
Treatment Options for a Deviated Septum
Numerous treatment modalities exist for addressing a deviated septum, encompassing non-surgical interventions and more invasive surgical techniques. All aim to mitigate symptoms and enhance nasal functionality.
Non-surgical and Surgical Options
Non-surgical interventions for a deviated septum encompass the utilization of decongestants, antihistamines, and nasal corticosteroid sprays to address symptoms and mitigate inflammation.
These non-surgical modalities are frequently efficacious in alleviating nasal congestion, enhancing respiratory function, and minimizing nasal discharge stemming from a deviated septum. Decongestants constrict blood vessels in the nasal passages, diminishing swelling and congestion. Antihistamines manage allergic responses that could exacerbate symptoms. Nasal corticosteroid sprays mitigate inflammation in the nasal passages, consequently augmenting airflow.
While these interventions can ameliorate symptoms, they do not rectify the septal deviation. In instances where conservative approaches prove inadequate, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the structural anomaly.
Managing Symptoms of a Deviated Septum
The management of deviated septum symptoms frequently involves a combination of home remedies and lifestyle modifications that aim to alleviate discomfort and enhance nasal airflow.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Home remedies for managing a deviated septum include utilizing saline nasal sprays to maintain moisture in the nasal passages and reduce congestion. In addition, humidifiers can introduce moisture into the air, thereby aiding in alleviating nasal congestion. Steam inhalation is another effective remedy, as it assists in clearing the nasal passages and offers relief. Furthermore, applying nasal strips during the night can facilitate the opening of nasal passages, thereby enhancing breathing.
Implementing lifestyle adjustments such as maintaining a healthy weight, adequate hydration, and avoiding allergens can further contribute to symptom management. Should home remedies fail to yield sufficient relief, seeking medical counsel to explore alternative treatment modalities is imperative.
Preventing a Deviated Septum
Preventing a deviated septum entails implementing proactive measures to safeguard the nasal passages and mitigate the risk of trauma, which could result in the misalignment of the nasal septum.
Tips for Reducing the Risk of Deviated Septum
To mitigate the likelihood of developing a deviated septum, it is imperative to avoid nasal trauma by utilizing protective headgear during activities that pose a risk, such as contact sports, and ensuring safe environments to minimize the occurrence of accidental injuries.
Furthermore, maintaining optimal nasal hygiene plays a critical role in preventing nasal injuries. Consistently rinsing the nasal passages with a saline solution can promote cleanliness and overall nasal health.
In addition, effective allergy management is paramount, as allergic responses can instigate nasal inflammation and congestion, thereby heightening the susceptibility to trauma. Timely intervention for nasal infections, such as sinusitis, can avert complications that may contribute to forming a deviated septum.
Enacting preemptive measures to safeguard the nasal passages is pivotal in fortifying against potential injuries.